一起来了解Java的Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式:
1、简介
首先Lambda表达式是属于Java8的 一个新特性,提供Java编程中对于函数式编程的支持,有助于代码的简洁,可以取代大半部分的匿名函数,尤其对于集合的遍历和集合的操作,极大的简化了代码。
Lambda表达式的主体:
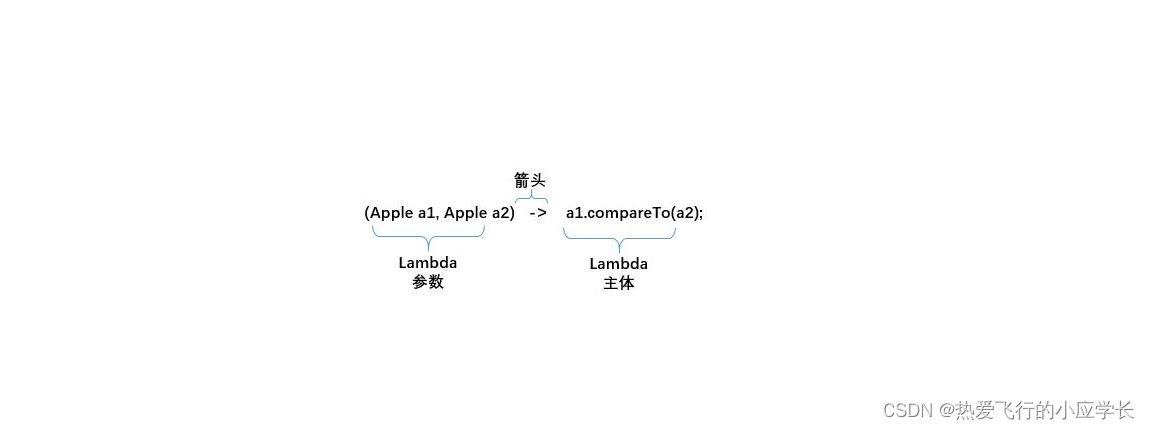
函数式接口:
注意:Lambda表达式一定要配合函数式接口一起使用,所谓函数式接口,就是接口中只有一个抽象方法的接口就是函数式接口,我们可以自定义,JDK也内置了大量的函数式接口。
1、@FunctionalInterface注解修饰了接口,那这个接口就是函数式接口,只能有一个方法,下面就是一个函数式接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyInteface {
void eat();
}
2、如果不加@FunctionalInterface**注解,你在接口里面只写一个抽象方法也可以认为是函数式接口:
public interface MyInteface {
void eat();
}
这样也是可以的。
3、函数式接口只有一种情况不只有抽象方法,那就是可以继承Object类的方法:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyInteface3 {
void eat();
@Override
String toString();
@Override
int hashCode();
}
2、Lambda表达式的使用:
1、在普通方法内的使用
Student类:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Student {
void eat();
}
测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student() {
//普通方法,重写并使用
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我是学生");
}
};
stu.eat();
//lambda表达式写法:
//参数1:重写了Student接口中唯一的那个无参数的eat抽象方法做了具体的实现,所以重写不 需要署名
//参数2:-> 表达式 固定的
//参数3:{具体的实现} 对Student接口中唯一的eat方法做了具体的实现
Student stu2 = () -> {
System.out.println("学生吃饭");
};
stu2.eat();
}
}
输出:
我是学生
学生吃饭
2、带参方法的使用
Student类:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Student {
void eat(String food);
}
测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda重写Student接口唯一的有参方法:
Student stu2 = (foodName)->{
System.out.println("学生在吃"+foodName);
};
stu2.eat("肉");
}
}
//输出:学生在吃肉
3、Lambda表达式实现多线程
之前在多线程(1)的那篇文章内有介绍了创建多线程的方法,这里就使用lambda来创建线程:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("这个线程是由lambda来创建的");
});
t.start();
}
}
4、Lambda表达式操作运算
我们使用lambda来操作运算可以少很多代码:
函数式接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Calculator<T> {
T operation(T v1,T v2);
}
测试类:
public class Test {
//计算方法
public static Integer operator(Integer v1,Integer v2,Calculator<Integer> calculator){
return calculator.operation(v1, v2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用lambda表达式:
//这里的意思就是传入两个参数,返回运行后的值
int add = Test.operator(5,10,(x,y)->{
return x+y;
});
//简写:可以少写很多代码,比上面更简介了
int num1 = Test.operator(5,10,(x,y)->x+y);
int num2 = Test.operator(10,5,(x,y)->x-y);
System.out.println(add);
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(num2);
}
}
输出:
15 、15 、5
5、Lambda表达式方法引用
有时候我们不是必须要要重写接口的方法来做具体的实现,我们如果有存在的方法能来实现,也可以通过方法 引用的方式来引用已经存在的方法做接口中方法具体的实现,这样的好处就是代码复用,比如下面这样:
函数式接口:
public interface ResultOneParam {
int method(int a);
}
测试类:
public class Test {
public int addTo(int a){
return a+10;
}
public static int addTo2(int a){
return a+10;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//lambda重写了method方法
ResultOneParam lambda1=(a)->a+10;
//方法引用:就是在Test里面的addTo2方法用来替代method被重写的方法
ResultOneParam lambda2= Test::addTo2;
int result1= lambda2.method(9);
System.out.println(result1);
//方法引用 ::引用现成的方法来替代方法重写,这样可以方法重用
Test test=new Test();
ResultOneParam lambda3=test::addTo;
int result2= lambda3.method(9);
System.out.println(result1);
}
}
6、Lambda表达式对集合的使用
当然Lambda对集合的操作也是很方便的,可以少些很多代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(5,1,3,4,5,0,9,7,0,1,5);
//lambda表达式遍历集合,重写了Consumer接口的方法
list.forEach((element)->{
System.out.println(element);
});
//简写:
list.forEach(element-> System.out.println(element));
//lambda表达式方法引用,用于遍历输出list集合:
list.forEach(System.out::print);
//输出list的偶数:
list.forEach(element->{
if(element%2==0){
System.out.println(element);
}
});
}
}
7、总结
好啦 以上就是Lambda表达式的一些基本用法
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注编程教程的更多内容!
前言线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见 的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串... 线性表在逻辑 ...
